Scalar Quantities
Visualize scalar-valued data at the nodes or cells of a sparse volume grid.
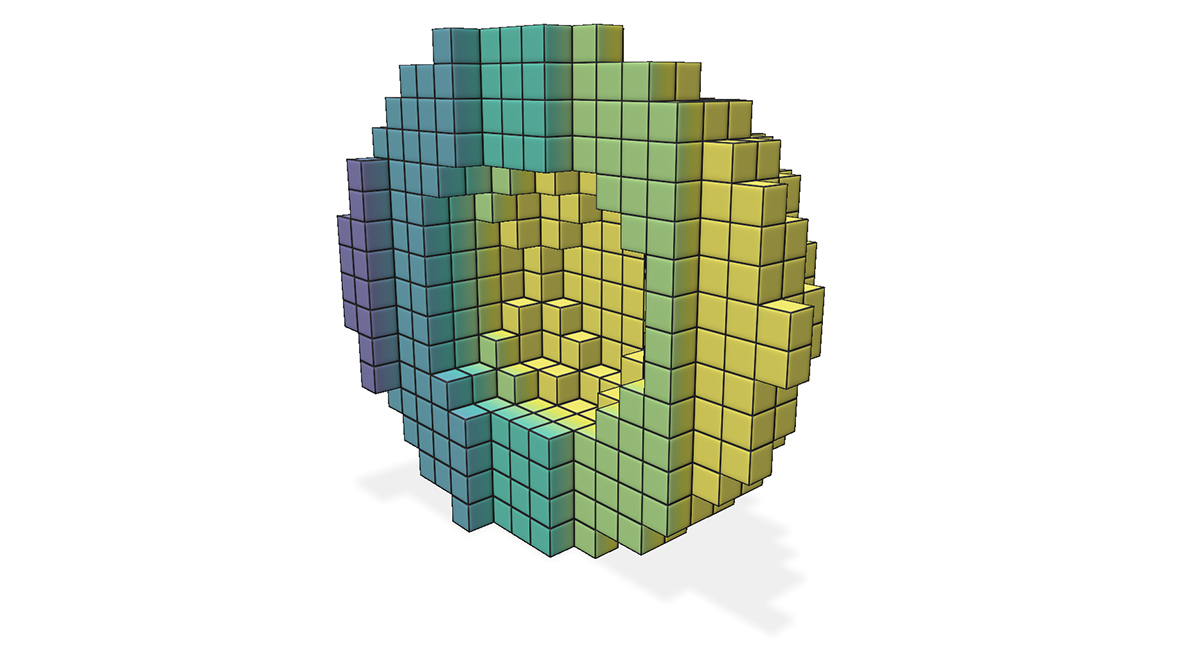
Example: adding scalar quantities to a sparse volume grid
import polyscope as ps
import numpy as np
ps.init()
origin = (0., 0., 0.)
cell_width = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1)
occupied_cells = np.array([
[0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0],
])
ps_grid = ps.register_sparse_volume_grid("sample sparse grid", origin, cell_width, occupied_cells)
# === Cell scalar: one value per occupied cell ===
cell_scalars = np.array([0.1, 0.5, 0.9, 0.3])
ps_grid.add_scalar_quantity("cell scalar", cell_scalars, defined_on='cells', enabled=True)
# === Node scalar: values at node indices ===
# For each cell (i,j,k), its corner nodes are (i+dx, j+dy, k+dz) for dx,dy,dz in {0,1}.
# Collect all unique nodes and provide a value for each.
node_set = set()
for cell in occupied_cells:
for dx in range(2):
for dy in range(2):
for dz in range(2):
node_set.add((cell[0]+dx, cell[1]+dy, cell[2]+dz))
node_indices = np.array(list(node_set), dtype=np.int32)
node_values = np.random.rand(len(node_indices)).astype(np.float32)
ps_grid.add_scalar_quantity("node scalar", node_values, defined_on='nodes',
node_indices=node_indices, enabled=True)
ps.show()
Add cell scalars¶
SparseVolumeGrid.add_scalar_quantity(name, values, defined_on='cells', datatype='standard', **scalar_args)
Add a scalar quantity defined at the cells of the grid.
namestring, a name for the quantityvaluesa numpy array of lengthn_cells, one value per occupied cell in the same order as theoccupied_cellsarray used at registrationdefined_onstring, must be'cells'datatypeone of'standard','symmetric','magnitude','categorical'
This function also accepts optional keyword arguments listed below, which customize the appearance and behavior of the quantity.
Add node scalars¶
SparseVolumeGrid.add_scalar_quantity(name, values, defined_on='nodes', node_indices=..., datatype='standard', **scalar_args)
Add a scalar quantity defined at the nodes of the grid.
Node values are passed as paired arrays of node indices and values. For a cell with grid indices (i, j, k), its corner nodes have indices (i+dx, j+dy, k+dz) for dx, dy, dz in {0, 1}. The node indices may be passed in any order, and extra entries (for nodes not required by any occupied cell) are ignored. However, all required node values must be present.
namestring, a name for the quantityvaluesa numpy array of lengthN, one scalar per nodedefined_onstring, must be'nodes'node_indicesan(N, 3)integer numpy array of node grid indices, required whendefined_on='nodes'datatypeone of'standard','symmetric','magnitude','categorical'
This function also accepts optional keyword arguments listed below, which customize the appearance and behavior of the quantity.
Categorical Scalars¶
Scalar quantities can also be used to visualize integer-valued labels such as categories, classes, segmentations, flags, etc.
Add the labels as a scalar quantity where the values just happen to be integers (each integer represents a particular class or label), and set datatype='categorical'. This will change the visualization to a different set of defaults, adjust some shading rules, and use a distinct color from the colormap for each label.
Color Bars¶
Each scalar quantity has an associated color map, which linearly maps scalar values to a spectrum of colors for visualization.
See colormaps for a listing of the available maps, and use add_scalar_quantity(..., cmap="cmap_name") to choose the map.
The colormap is always displayed with an inline colorbar in the structures panel, which also gives a histogram of the scalar values in your quantity.
The limits (vminmax) of the colormap range are given by the two numeric fields below the colored display. You can click and drag horizontally on these fields to adjust the map range, or ctrl-click (cmd-click) to enter arbitrary custom values.
onscreen colorbar
Optionally an additional onscreen colorbar, which is more similar to the colorbars used in other plotting libraries, can be enabled with add_scalar_quantity(..., onscreen_colorbar_enabled=True).
By default it is positioned automatically inline with the other UI elements, or it can be manually positioned with add_scalar_quantity(..., onscreen_colorbar_location=(400., 400.)).
You can even export this color map to an .svg file for creating figures via the options menu.
Scalar Quantity Options¶
When adding a scalar quantity, the following keyword options can be set. These are available for all kinds of scalar quantities on all structures.
Keyword arguments:
enabledboolean, whether the quantity is initially enabled (note that generally only one quantitiy can be shown at a time; the most recent will be used)datatype, one of"standard","symmetric","magnitude", or"categorical", affects default colormap and map range, and the categorical policies mentioned abovevminmax, a 2-tuple of floats, specifying the min and max range for colormap limits; the default isNone, which computes the min and max of the data- colormap keywords:
cmap, which colormap to useonscreen_colorbar_enabledset toTrueto enable an additional traditional colormaponscreen_colorbar_locationset to screen coordinates like(400., 400.)to position the onscreen colorbar manually (default is automatic)
- isoline keywords (darker-shaded stripes showing isocontours of the scalar field):
isolines_enabledare isolines enabled (default:False)isoline_styleone ofstripe,'contour(default:stripe)isoline_periodhow wide should the darkend stripes be, in data units (default: dynamically estimated)isoline_period_relativeif true, interpret the width value as relative to the world coordinate length scale (default:False)isoline_darknesshow much darker should the alternating stripes be (default:0.7)isoline_contour_thicknesshow thick should the contour lines be (default:0.3)
If not specified, these optional parameters will assume a reasonable default value, or a persistent value if previously set.