Sparse Volume Grids¶
Sparse volume grid structures visualize data defined on a sparse subset of cells in an axis-aligned 3D grid. Unlike the dense Volume Grid, a sparse volume grid only stores and renders the cells you specify, making it well-suited for adaptive grids, occupancy maps, and other data that occupies only a portion of a regular grid.
As usual, first you register a sparse volume grid by specifying a grid origin, cell size, and list of occupied cells. Then you can add quantities such as scalar or color data defined per-cell or per-node.
Example: registering a sparse volume grid and adding a scalar quantity
#include "polyscope/polyscope.h"
#include "polyscope/sparse_volume_grid.h"
polyscope::init();
// define the grid parameters
glm::vec3 origin{0., 0., 0.};
glm::vec3 cellWidth{0.1, 0.1, 0.1};
// list of occupied cells by their integer grid indices
std::vector<glm::ivec3> occupiedCells = {
{0, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 1},
};
// register the grid
polyscope::SparseVolumeGrid* psGrid = polyscope::registerSparseVolumeGrid(
"sample sparse grid", origin, cellWidth, occupiedCells);
// add a scalar function on the grid (one value per cell)
std::vector<float> cellScalars(occupiedCells.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < cellScalars.size(); i++) cellScalars[i] = static_cast<float>(i);
psGrid->addCellScalarQuantity("cell scalar", cellScalars);
polyscope::show();
Registering a sparse volume grid¶
Origin and cell width
The origin parameter specifies the position of the node/corner origin of the grid. Cell (0,0,0) has its lower-left corner at the origin. If you are thinking in terms of cell centers, shift the origin you pass in by half a cell width: origin = cellCenter - 0.5 * cellWidth.
The cellWidth parameter gives the size of each grid cell along each axis. All cells have the same size.
polyscope::registerSparseVolumeGrid(std::string name, glm::vec3 origin, glm::vec3 gridCellWidth, const T& occupiedCells)
Add a new sparse volume grid structure to Polyscope.
namethe name of the structureoriginaglm::vec3giving the xyz position of the node/corner origingridCellWidthaglm::vec3giving the width of each cell along each axisoccupiedCellsan array ofglm::ivec3giving the integer grid indices of all occupied cells. The type should be adaptable to an array ofglm::ivec3.
Render modes¶
The sparse volume grid supports two render modes, controlled by SparseVolumeGrid::setRenderMode():
SparseVolumeGridRenderMode::Gridcube(default) renders each occupied cell as a filled cube. Quantities are visualized on the cube faces.SparseVolumeGridRenderMode::Wireframerenders only the grid outline as wireframe edges. This mode is useful for seeing through the grid to inspect its structure. Quantities are not drawn in wireframe mode.
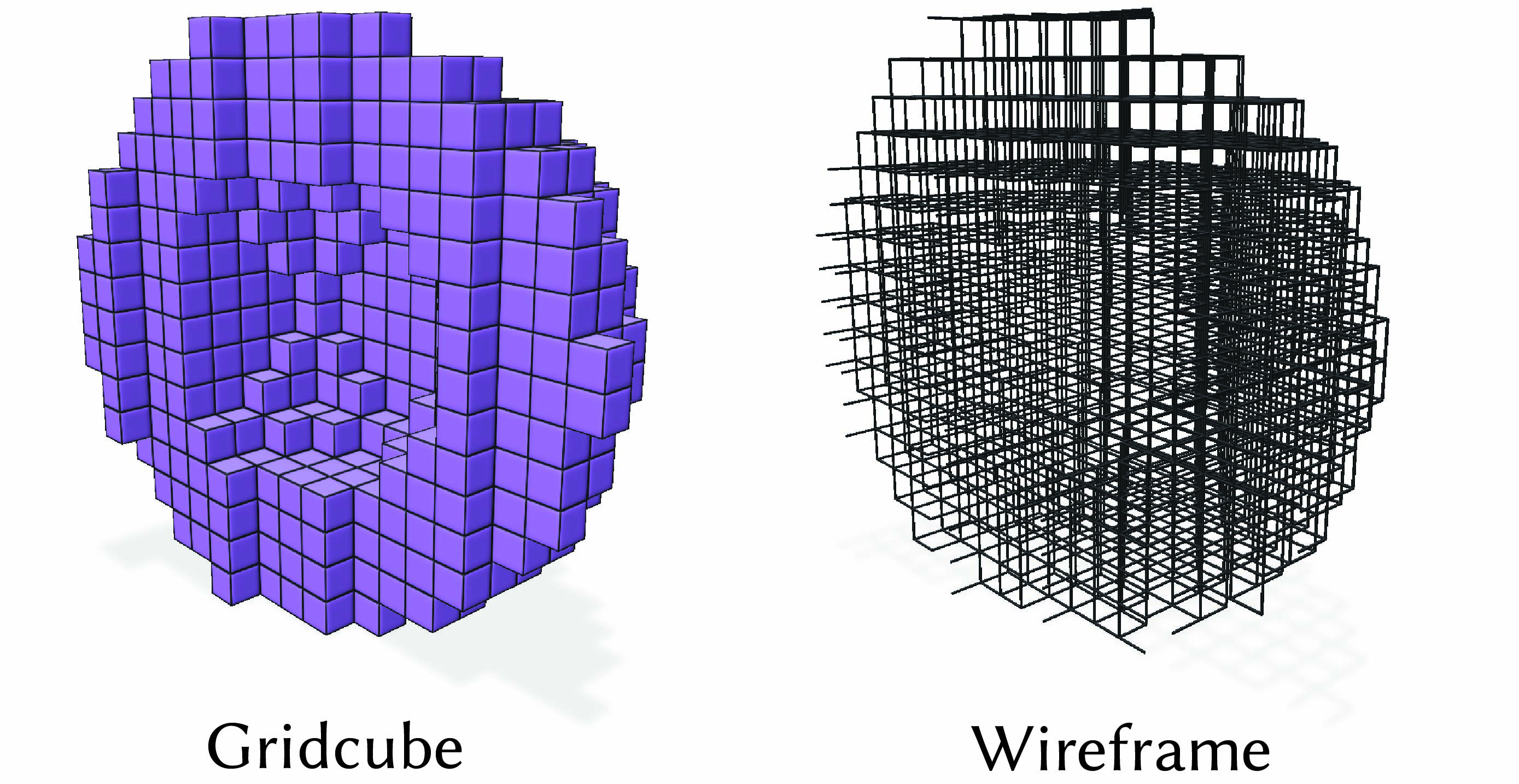
The wireframe appearance can be adjusted with SparseVolumeGrid::setWireframeRadius() and SparseVolumeGrid::setWireframeColor().
polyscope::SparseVolumeGrid* psGrid = polyscope::registerSparseVolumeGrid(
"sample sparse grid", origin, cellWidth, occupiedCells);
psGrid->setRenderMode(SparseVolumeGridRenderMode::Wireframe);
psGrid->setWireframeRadius(0.5);
psGrid->setWireframeColor(glm::vec3{1.f, 0.f, 0.f});
Slice planes¶
As shown in the video above, slice planes are useful for inspecting the structure of a sparse volume grid. Slice planes can be manipulated programmatically or manually in the GUI; see the slice plane documentation for more details.
Picking¶
“Picking” refers to selecting and inspecting elements by clicking on the object in the scene. Picking sparse volume grid elements works similarly to other structures, see the overview of Selection / Picking for general information.
By default, only cells can be selected, until you have added some data on nodes. You can override this behavior by calling SparseVolumeGrid::markNodesAsUsed(), to act as if a node quantity had been added.
As with other structures, you can call interpretPickResult() to get additional info about a click.
struct SparseVolumeGridPickResult {
SparseVolumeGridElement elementType; // which kind of element was clicked (enum values: {CELL, NODE})
glm::ivec3 cellIndex; // integer grid index of the clicked cell (only populated if cell)
uint64_t cellFlatIndex; // flat index into the occupied cells array (only populated if cell)
glm::ivec3 nodeIndex; // integer grid index of the clicked node (only populated if node)
};
SparseVolumeGridPickResult SparseVolumeGrid::interpretPickResult(PickResult result)
Get additional information about a click, specific to this structure type (if it was the structure which was clicked on).
Options¶
See structure management for options common to all structures such as enabling/disabling, transforms, and transparency.
| Parameter | Meaning | Getter | Setter | Persistent? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| color | the color of the volume | glm::vec3 getColor() |
setColor(glm::vec3 val) |
yes |
| edge width | how thick to draw mesh edges, use 0. to disable and 1. for reasonable edges |
double getEdgeWidth() |
setEdgeWidth(double val) |
yes |
| edge color | the color of the grid edges | glm::vec3 getEdgeColor() |
setEdgeColor(glm::vec3 val) |
yes |
| cube size factor | shrink factor from 0-1 to draw gaps between cells, 0 is no shrink (default) | double getCubeSizeFactor() |
setCubeSizeFactor(double val) |
yes |
| material | what material to use | std::string getMaterial() |
setMaterial(std::string name) |
yes |
| render mode | how to render the voxels: Gridcube (default, filled cubes) or Wireframe (grid outline only) |
SparseVolumeGridRenderMode getRenderMode() |
setRenderMode(SparseVolumeGridRenderMode mode) |
yes |
| wireframe radius | relative radius for wireframe spheres/cylinders; 1 means radius is half the smallest cell width |
double getWireframeRadius() |
setWireframeRadius(double val) |
yes |
| wireframe color | color used for wireframe rendering | glm::vec3 getWireframeColor() |
setWireframeColor(glm::vec3 val) |
yes |