Materials
Polyscope uses matcaps to render the appearance of objects in the scene, as opposed to more traditional configurations of lights and shading models, etc. A matcap is a small image of a material, which is sampled by the renderer to query the materials’ appearance from a some angle. Scene information like lighting is implicitly baked in to the matcap image.
Most objects in Polyscope (surface meshes, point clouds, vectors, etc) expose a material='matname' option to choose a material for the object’s appearance. Additionally, materials can generally be set in the UI from [Options] --> [Material].
Blended materials¶
In Polyscope, we often want to adjust set custom colors for rendered objects. This can be a constant color for the object (to distinguish structures in a scene), or a varying color across a surface (when color-mapping scalar quantities). Traditionally, matcaps don’t really support setting an albedo color like this, but we achieve the effect in Polyscope by blending between basis matcaps.
How it works
Instead of just using a single material image, we take four images of the material, representing basis red, green, blue, and black components.




At runtime, to generate a color from a triple of rgb values each in the range [0,1], we sample the images like:
outputColor = r * basis_r + g * basis_g + b * basis_b + (1. - r - g - b) * basis_k
Intuitively, this strategy presumes the underlying material has a light response which is a linear function of the color, plus another component which is independent of the color. Crucially, Polyscope uses a linear lighting workflow and performs this blending on linear matcaps before tone-mapping, which is necessary for the results to look reasonable across the full color space.
Materials which which support this blending are denoted by (rgb) in the options menu. Ordinary static matcaps consisting of a single image can still be used as materials, but will ignore any color maps or other options.
Preserving colors with the flat material¶
Generally, Polyscope applies material shading and tone-mapping to render 3D content. However, this means that data such as colors and tonemapped scalars will be a somewhat different color on-screen compared to what is in the data.
The flat material is special: it not only applies flat coloring with no shading effects, but furthermore cancels-out tonemapping and other effects to ensure that the color you see onscreen is exactly the same as the data specified.
Use the flat material any time you need exact color reproduction.
Built-in materials¶
Polyscope supports the following built-in materials:
| Name | String Key | Blendable | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| clay | clay |
yes |  |
| wax | wax |
yes |  |
| candy | candy |
yes |  |
| flat | flat |
yes |  |
| mud1 | mud |
no | 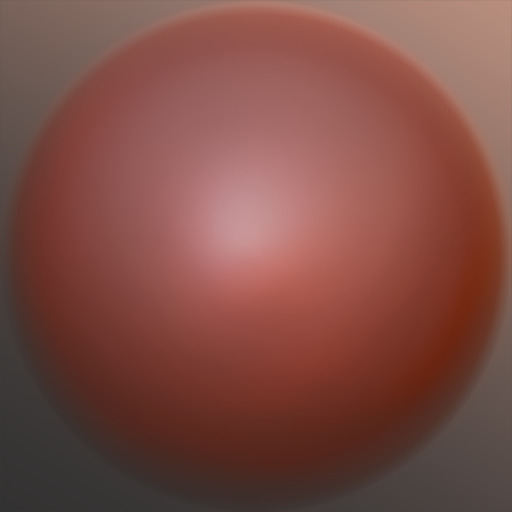 |
| ceramic1 | ceramic |
no |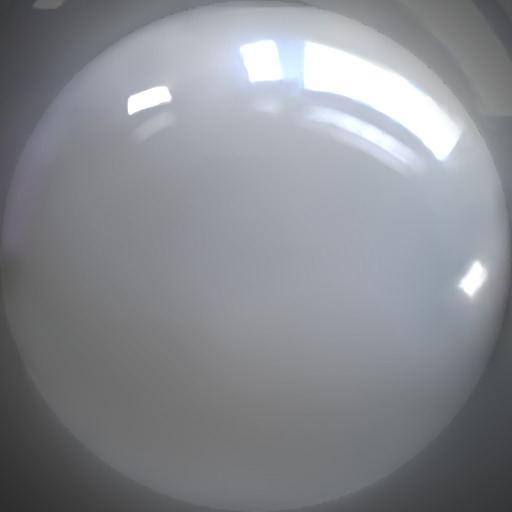  |
| jade1 | jade |
no | 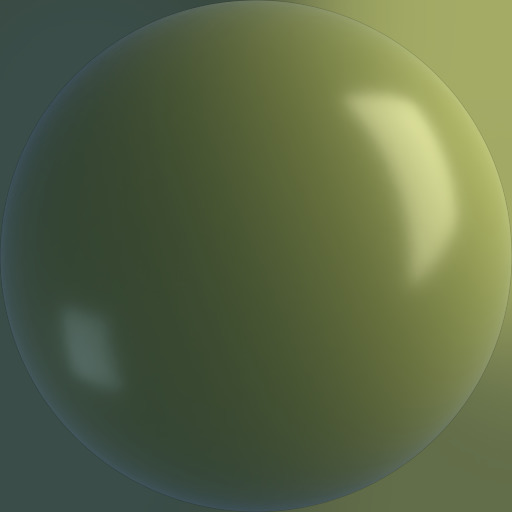 |
| normal1 | normal |
no |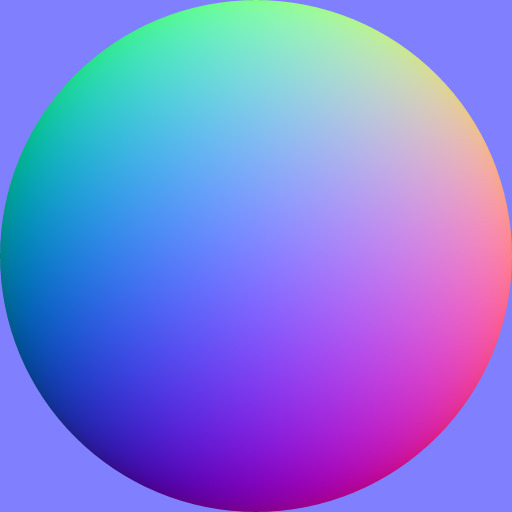  |
Loading custom materials¶
Custom matcaps can be loaded at runtime from image files and used anywhere materials are used. Loading can be performed with the UI from [Appearance] --> [Materials] --> [Load material], or programatically using the function below. For blendable matcaps, if the single filename mat.hdr is given, Polyscope will try to load mat_r.hdr, mat_g.hdr, etc.
Ideally, matcap images should be linear .hdr images for best results, but any image will work. If other image formats are given, the input is assumed to be non-linear and will be inverse-tonemapped with intensity=1 and gamma=2.2 before use. Most common image formats are accepted (anything stb_image can read).
load_static_material(mat_name, filename)
load_static_material¶
Load a new static (non-blendable) material from a single image file filename. The new material will be called mat_nam.
Example:
import polyscope as ps
ps.load_static_material("fancy mat", "my_image.png")
load_blendable_material(mat_name, filenames=None, filename_base=None, filename_ext=None)
load_blendable_material¶
Load a new blendable material, which will be called matName.
There are two different ways to specify which files to load the material images from:
- Specify
filenames, a tuple of four string filenames corresponding to red, green, blue, and black basis materials - Specify
filename_base, andfilename_ext, to generate the four filenames asfilename_base + "_r" + filename_ext, etc.
Example:
import polyscope as ps
ps.load_blendable_material("fancy blendable mat", filenames = (
"my_image_r.png",
"my_image_g.png",
"my_image_b.png",
"my_image_k.png"
))
# OR
ps.load_blendable_material("fancy blendable mat", filename_base="my_image", filename_ext=".png")
-
The matcaps are from the Blender matcap repository, available under a CC0/public domain license. Thanks to the Blender community for contributing them! ↩↩↩↩